Design and Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Printed Air-Core Transformers for High-Frequency Power Applications
Journal
Abstract
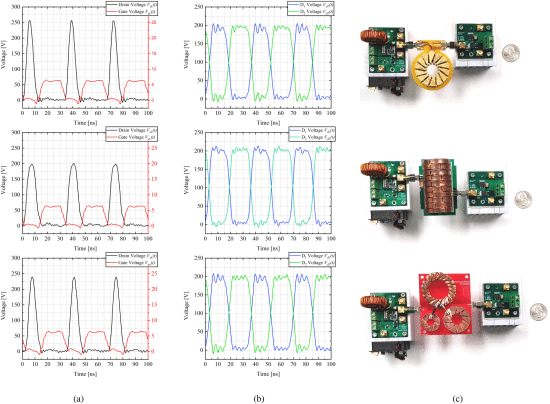
This article presents various designs of toroidal air-core transformers utilizing a 3-D printing and electroplating fabrication methodology. For certain applications and switching frequency regimes, limitations in core-based magnetics force circuit designers to use air-core components, which are conventionally wire-wound, and thus, constrained to simple structures with poor copper coverage. 3-D printing offers a solution to this constraint and provides more flexibility for transformer designs. This article includes design calculations, finite-element method (FEM) simulations, and loss analysis for three different toroidal transformer designs: one which features nested toroids, coupling their N 2 flux, the second which uses stacked toroids, coupling the one-turn flux, and the third which interleaves two windings. Furthermore, the manufacturing procedure presented in this article allows for accurate modeling of the transformer’s inductance matrix, which is advantageous over hand-wound air-core components. Additionally, we provide experimental demonstrations, including the implementation of these transformers in 100-W, 30-MHz resonant converters. Lastly, COMSOL FEM design automation MATLAB scripts for the various inductors and transformers discussed in this article are publicly available in the paper by Z. Tong (2019), allowing for fast parametric modeling of magnetic designs.