Active Power Device Selection in High- and Very-High-Frequency Power Converters
Journal
IEEE TPELS
Abstract
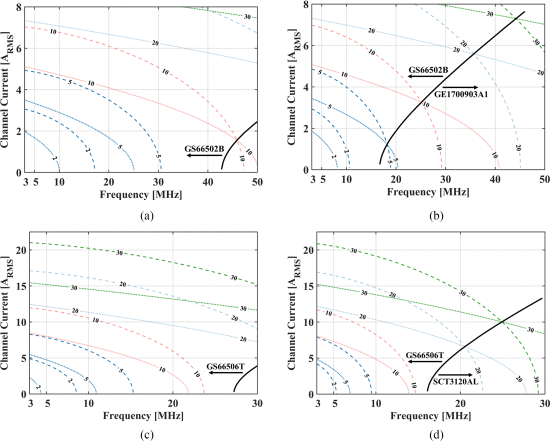
This paper aims to provide a road map for selecting power devices in soft-switched, megahertz (MHz) frequency power converters. Minimizing C OSS losses, which occur when charging and discharging the parasitic output capacitor of power semiconductors, is critical to efficient operation. These losses are excluded from manufacturer-provided information, and measurements are either sparse or not reported at all in the existing literature. We report the first high-frequency C OSS loss data from silicon carbide (SiC) power MOSFETs, with a range of devices tested from 1 to 35 MHz and up to 800 V. In contrast to GaN HEMTs, C OSS losses in SiC MOSFETs do not increase with dV/dt at these frequencies. A total of 3%-10% of the stored energy is dissipated in the measured SiC MOSFETs. We report new C OSS loss measurements for vertical silicon MOSFETs and expand on existing measurements for superjunctions, finding high variance in C OSS losses between devices for both constructions. High C OSS losses preclude the tested silicon MOSFETs from efficient operation at MHz frequencies. Lastly, we compare devices in soft-switched applications using a loss calculation that includes these COSS losses, and demonstrate a 100 W, 17 MHz dc-RF inverter using a custom-packaged SiC MOSFET.