Design of a Class-DE Rectifier with Shunt Inductance and Nonlinear Capacitance for High-Voltage Conversion
Journal
IEEE TPELS
Abstract
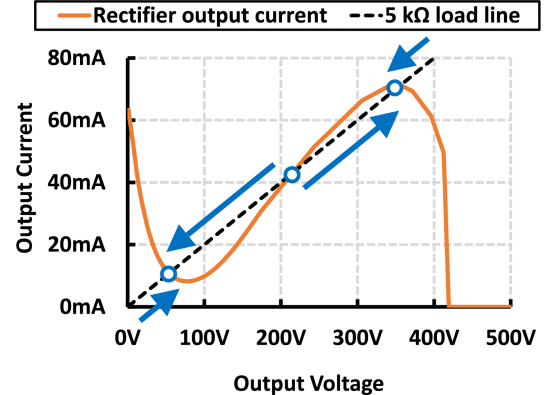
This paper presents a design method for a resonant class-DE rectifier with a shunt inductance input network. The cass-DE resonant rectifier offers numerous advantages at high operating frequencies and high output voltages. For a high-voltage design, the limiting factor has been the absence of a design process incorporating shunt inductance for low-to-high impedance matching as well as nonlinear capacitance from semiconductor devices. To design a rectifier with a specific input impedance at the fundamental frequency of operation, designers have been relying on either parametric variation in iterative simulations that often takes a long time to complete, or simple equations without considering nonlinear capacitances that renders the analysis inaccurate at high frequencies. In this paper, we propose a design procedure that begins with universal design curves that are applicable regardless of the capacitance nonlinearity. This is followed by parameter selection and a convergence check to ensure the rectifier operates at the desired output voltage. Based on the outlined procedure, we design and experimentally verify a 27-MHz 350-V current-driven rectifier, a 25-MHz 500-V voltage-driven rectifier, and a 27.12-MHz 2-kV four-stage rectifier, all of which the resonant capacitor is nonlinear and the input impedance is resistive at the switching frequency.