3-D-Printed Air-Core Inductors for High-Frequency Power Converters
Journal
IEEE TPELS
Abstract
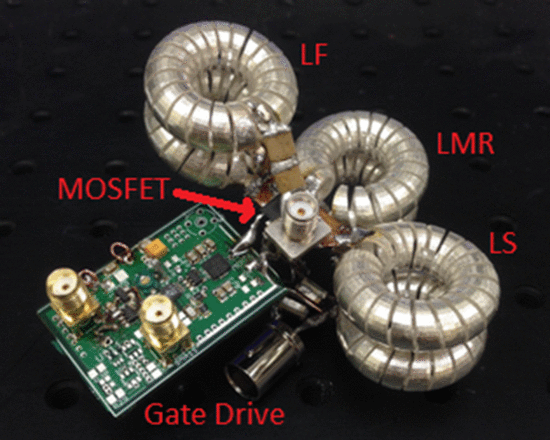
This paper presents the design, modeling, and characterization of 3-D-printed air-core inductors for high-frequency power electronics circuits. The use of 3-D modeling techniques to make passive components extends the design flexibility and addresses some of the fabrication limitations of traditional processes. Recent work [1]- [9] has demonstrated the feasibility of incorporating air-core inductors in high-frequency (>10 MHz) switching power converters. These implementations have used discrete wire wound solenoids and toroids, and planar components that use printed circuit board traces or microfabrication techniques to make air-core inductors. However, realizations of such components have limitations in performance and applicability including open paths conducive to the flow of leakage fields, and difficulties in achieving optimal cross section to minimize loss. Along with the current effort of involving 3-D printing technology to make inductors [10], [11], we propose the use of 3-D printing and casting/plating techniques as a simple and accessible alternative that adds flexibility and functionality to the air-core inductor design for high-frequency power conversion at moderate to high-power (e.g., tens to thousands of watts) and high-voltage (greater than 100 V) levels. In this paper, we present several examples of air-core inductors realized using 3-D printing and casting/plating techniques to give an idea of the geometries that are possible to design. Moreover, we show that some of these designs can lead to improved electrical performance. This paper also describes the tools used by the authors to design, fabricate, and characterize the electromagnetic performance of the air-core inductors. The software used to generate the 3-D scaffolds for the inductors are freely available and easily accessible. Readers are encouraged to explore more possibilities of geometries that can lead to better performance with the ease of manufacturing. As progress in additive manufacturing continues, we envision 3-D printing of a complete scaffold structure that after plating (or casting) will contain all resonant passive components of an RF switching converter. Toward this goal, we present a 70-W prototype 27.12-MHz resonant inverter that incorporates some of the 3-D-printed components developed for this paper.